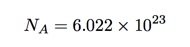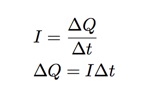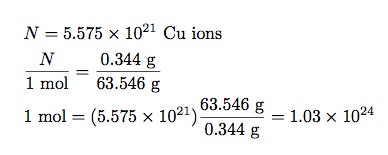- Andy
- Beef on Weck
- Being a Mother
- Chili Cook-off
- Communication (Gazebo)
- Daddy
- Everyone has an Angel
- Family
- Gonna be a Bear
- Harrison Bergeron
- Mute and Alone
- Privacy Policy
- Rikki-tikki-tavi
- Scientists Study Grizzly Bears
- Ship vs. Lighthouse
- Snowvember (Buffalo 2014)
- Somebody…
- The Present
- The Soldier
- The Star
- Winter
- 11foot8.com
- 365 Tomorrows
- 7 into 28
- A Tale of Two Brains
- Alien to Covenant – History of Alien
- Am I Unique
- AMARC
- American Muscle Car Museum
- Andre Rieu
- Antipodes Map
- Ark in Space
- Azure Status
- Blizzard of '77
- Broken Chains
- CDC – Flu
- Christmas Forever AZ
- Coldest City on Earth
- Creations for Charity (Lego)
- Cruise.com
- Curb Watching
- D&D Beyond
- D&D Beyond to FG Character Converter
- Daily Fuel Gauge Report
- Dinosaur Earth
- DMs Guild
- Dofo
- Dr. Demento
- DriveThru RPG
- Dungeon in a Box
- Dyson’s Dodecahedron
- Fantasy Name Generator
- Farmer's Donkey
- Fast Character
- Flight Aware
- Flight Radar 24
- Flixable
- Gaming Table
- Genius
- Geo Guesser!
- Hack The Menu
- Hackers for Charity
- Hadzy
- Have I been Pwned
- HexRoll
- How to remove a tick (properly)
- Identity Theft Resource Center
- Leak Lookup
- Line Rider – Hall of the Mountain King
- Make My Drive Fun
- Mapologies
- Marine Traffic
- MathPapa
- MechWarrior Online
- Medieval Murder Maps
- Meteor Shower Calendar
- Mini Building Materials
- Monterey Bay Aquarium
- MyAbandonware
- Nah! I just might be in there!
- National Do Not Call Registry
- No More Ransom
- NOAA – Louisville
- Nobody Live
- Norse Cyber Attack Map
- OCEARCH.org
- Omega Game Shrine
- Out of the Woods Forestry
- Overt
- PC Gaming Wiki
- Percheron
- Periodic Stats
- Periodic Videos (TED)
- Permethin Fact Sheet
- Pigeon Key Foundation
- Project 44
- pTable
- Pumpkin Pile
- Random Restaurant Generator
- Rankin/Bass – Wikipedia
- ReelGood
- RockAuto
- Roll20 Enhancement Suite
- Schimpff's
- Scuba Shooters
- Sinking of the Titanic
- Smoky Mountain Fall Foliage Map
- Speedsums
- SR-71 Speed Check
- Steam Status
- Still Tasty
- StreamSquid
- Sunken Ships of the Second World War
- Super Slice!
- Swedish Fish
- Tank America
- Taste Dive
- TBSP (TaBleSPoon)
- The Louvre
- The Oz Museum
- The Strong National Museum of Play
- They Can Talk
- This Beat Goes on/Switchin' to Glide
- Tick Removal (CDC)
- Trappistine Candy
- Vacation Rentals By Owner
- Vehicle Privacy Report
- VPNFilter Check
- War Puppets Rise to Heaven
- Weather Back Home
- WebGL Water
- Whalers on the Moon
- What's New on Netflix
- Who's On First
- Why are Jacks called Jacks?
- Wild Spirit
- Window Swap
- WKRP Turkey Drop
- Wordcount
- World's Hottest Chocolate Bar
- WWII Portraits of Honor
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- July 2011
- June 2011
- May 2011
- April 2011
The Headless Horseman
Posted in Because I Can
Mole Day
October 23rd is Mole Day—you know, because 10/23 is like 1023.
THE EARLY HISTORY of chemistry has many interesting stories. Just consider the problems scientists had 200 years ago as they tried to figure out some of the most basic ideas of chemistry. It was clear that there were different substances—for instance, water is different than coal. But it wasn’t so clear what these substances were made of. You could take something like nitrogen gas (N2) and oxygen gas (O2) and combine them together to make another gas (in this case NO2). It thus seemed reasonable to suppose that stuff (molecular gas) was made of smaller stuff (atoms). But the evidence isn’t so easy to see. The primary difficulty is that humans can’t see molecules or atoms. All the scientific ideas have to be built on indirect evidence.
This is where Amedeo Avogadro comes into the picture (of course his real name is Lorenzo Romano Amedeo Carlo Avogadro di Quaregna e di Cerreto—but everyone just calls him Avogadro for obvious reasons). Avogadro developed the following idea:
Avogadro’s Law: If you have two gasses at the same temperature and pressure, they will occupy the same volume only if they contain the same number of molecules.
If you are thinking this is just a version of the Ideal Gas Law, you are correct—but let’s move on to a useful example. Suppose you take water (which is H2O) and run an electric curent through it—called electrolysis. This can break the water molecules into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas (which you could collect). If you had these two gases at the same temperature and pressure, the hydrogen gas would take up twice the volume compared to the oxygen gas. Why? Well, when you break up the water molecule, you get twice as much hydrogen as oxygen. Yes, hydrogen doesn’t just float around as a single atom. Instead it forms a bond with another hydrogen to make H2—but oxygen does the same thing (O2).
In the end, you would know that water is made of both hydrogen and oxygen and that there is twice as much hydrogen as oxygen. That’s a pretty big piece to the whole elements puzzle and you need an idea like Avogadro’s Law to figure it out.
Avogadro’s Number
But what about this number of Avogadro? Why is it important and why didn’t Amedeo know what it was? Let’s start with a definition. If I have 12 grams of carbon-12 (not any other isotopes of carbon) then it would have exactly Avogadro’s number of atoms in it. We can write this number as (approximately):
So we would call this number of carbon atoms, one mole (sort of like 12 eggs is one dozen).
Why is important? Avogadro’s number is sort of like a bridge. It bridges chemistry and atomic physics. In chemistry we measure things based on their bulk properties. Things like mass (total mass), pressure, volume, temperature. However, when we consider these things from an atomic perspective we look at individual atoms and the momentum, velocity of these particles. Avogadro’s number connects these two ideas and allows us to explore atomic-level things by measuring macroscopic level quantities. It’s a big deal.
But why didn’t Avogadro know this number? Because he didn’t directly come up with the idea. Chemists named the number after Avogadro to honor his contributions to chemistry.
Determining a Value for Avogadro’s Number
If you had a carton with a dozen eggs, you could open up the package and count the number of eggs to find out that one dozen equals twelve. You can’t really do the same thing with a mole of carbon. Carbon atoms are too tiny to see and there are too many to count. We have to find another way to get a value for Avogadro’s number. There are quite a few ways to determine this magic number, but let me go over a simple method.
Start with two pieces of copper placed in a solution of copper-sulfate. When you run an electric current through the system, copper is removed from one plate and deposited on the other plate. This means that one of the plates gains mass and the other loses mass (should be by the same amount).
When the copper atom is removed from one plate, it acts as a charge carrier in the complete circuit (battery, wires, copper, solution). If I measure the current in this circuit and record the time, I can use the definition of current to find the total transfer of charge (which would be the transfer of copper ions).
Let’s put this all together.
- Run current through the copper and copper sulfate.
- Positive copper ions are transferred from one plate to the other making a change in mass (which I can measure).
- I can measure the current and time and calculate the total transfer of charge from one plate to another.
- Since a copper ion has a positive charge of 1 e (charge of an electron), I can get the number of ions transferred.
- Knowing that 1 mole of copper is 63.546 grams, I should be able to get a relationship between the change in mass and the number of moles—which will give me Avogadro’s number.
In my rough experiment, I had an electric current of 0.42 Amps for 10 minutes. This gives a total change in charge of 252 Coulombs. Dividing this by the charge of one ion (1.6 x 10-19 C) I get 5.575 x 1021 ions. The change in mass of one plate is 0.344 grams. That’s all I need. Now I can write:
That’s not a terrible value for Avogadro’s number. Really, it’s not. If you take the accepted value of 6.022 x 1023, then my estimate is just off by less than a factor of 2. I call that close enough. The idea works even if my method was a little bit sloppy. Still, my value is better than no value.
Posted in Because I Can
Vincent Price Performs Thriller!
On Friday the 13th in February in 1987, the legendary Vincent Price showed up as a guest on the Late Show starring Joan Rivers. While on the show, Price performed his classic segment from Michael Jackson’s “Thriller”.
Posted in Because I Can, Music, The Little Screen (Television)
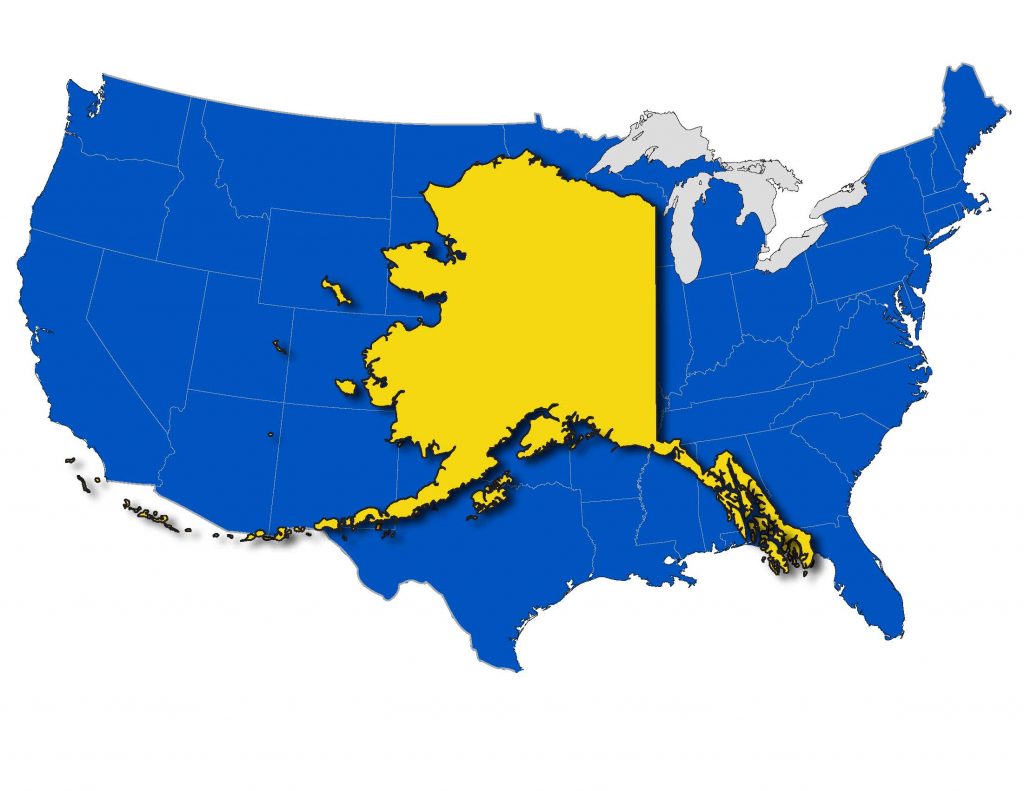
Anniversary of the Alaska Purchase
On this day in 1867, the U.S. formally takes possession of Alaska after purchasing the territory from Russia for $7.2 million, or less than two cents an acre. The Alaska purchase comprised 586,412 square miles, about twice the size of Texas
Posted in Events
Anniversary of Yeager Breaking the Sound Barrier

U.S. Air Force Captain Chuck Yeager becomes the first person to fly faster than the speed of sound.
Yeager, born in Myra, West Virginia, in 1923, was a combat fighter during World War II and flew 64 missions over Europe. He shot down 13 German planes and was himself shot down over France, but he escaped capture with the assistance of the French Underground. After the war, he was among several volunteers chosen to test-fly the experimental X-1 rocket plane, built by the Bell Aircraft Company to explore the possibility of supersonic flight.
For years, many aviators believed that man was not meant to fly faster than the speed of sound, theorizing that transonic drag rise would tear any aircraft apart. All that changed on October 14, 1947, when Yeager flew the X-1 over Rogers Dry Lake in Southern California. The X-1 was lifted to an altitude of 25,000 feet by a B-29 aircraft and then released through the bomb bay, rocketing to 40,000 feet and exceeding 662 miles per hour (the sound barrier at that altitude). The rocket plane, nicknamed “Glamorous Glennis,” was designed with thin, unswept wings and a streamlined fuselage modeled after a .50-caliber bullet.
Because of the secrecy of the project, Bell and Yeager’s achievement was not announced until June 1948. Yeager continued to serve as a test pilot, and in 1953 he flew 1,650 miles per hour in an X-1A rocket plane. He retired from the U.S. Air Force in 1975 with the rank of brigadier general.
Posted in On This Day, Planes Trains and Automobiles
White Christmas

White Christmas is a 1954 movie starring Bing Crosby and Danny Kaye that featured the songs of Irving Berlin, including the titular White Christmas.
Posted in Because I Can, On This Day, The Little Screen (Television)