- Andy
- Beef on Weck
- Being a Mother
- Chili Cook-off
- Communication (Gazebo)
- Daddy
- Everyone has an Angel
- Family
- Gonna be a Bear
- Harrison Bergeron
- Mute and Alone
- Privacy Policy
- Rikki-tikki-tavi
- Scientists Study Grizzly Bears
- Ship vs. Lighthouse
- Snowvember (Buffalo 2014)
- Somebody…
- The Present
- The Soldier
- The Star
- Winter
- 11foot8.com
- 365 Tomorrows
- 7 into 28
- A Tale of Two Brains
- Alien to Covenant – History of Alien
- Am I Unique
- AMARC
- American Muscle Car Museum
- Andre Rieu
- Antipodes Map
- Ark in Space
- Azure Status
- Blizzard of '77
- Broken Chains
- CDC – Flu
- Christmas Forever AZ
- Coldest City on Earth
- Creations for Charity (Lego)
- Cruise.com
- Curb Watching
- D&D Beyond
- D&D Beyond to FG Character Converter
- Daily Fuel Gauge Report
- Dinosaur Earth
- DMs Guild
- Dofo
- Dr. Demento
- DriveThru RPG
- Dungeon in a Box
- Dyson’s Dodecahedron
- Fantasy Name Generator
- Farmer's Donkey
- Fast Character
- Flight Aware
- Flight Radar 24
- Flixable
- Gaming Table
- Genius
- Geo Guesser!
- Hack The Menu
- Hackers for Charity
- Hadzy
- Have I been Pwned
- HexRoll
- How to remove a tick (properly)
- Identity Theft Resource Center
- Leak Lookup
- Line Rider – Hall of the Mountain King
- Make My Drive Fun
- Mapologies
- Marine Traffic
- MathPapa
- MechWarrior Online
- Medieval Murder Maps
- Meteor Shower Calendar
- Mini Building Materials
- Monterey Bay Aquarium
- MyAbandonware
- Nah! I just might be in there!
- National Do Not Call Registry
- No More Ransom
- NOAA – Louisville
- Nobody Live
- Norse Cyber Attack Map
- OCEARCH.org
- Omega Game Shrine
- Out of the Woods Forestry
- Overt
- PC Gaming Wiki
- Percheron
- Periodic Stats
- Periodic Videos (TED)
- Permethin Fact Sheet
- Pigeon Key Foundation
- Project 44
- pTable
- Pumpkin Pile
- Random Restaurant Generator
- Rankin/Bass – Wikipedia
- ReelGood
- RockAuto
- Roll20 Enhancement Suite
- Schimpff's
- Scuba Shooters
- Sinking of the Titanic
- Smoky Mountain Fall Foliage Map
- Speedsums
- SR-71 Speed Check
- Steam Status
- Still Tasty
- StreamSquid
- Sunken Ships of the Second World War
- Super Slice!
- Swedish Fish
- Tank America
- Taste Dive
- TBSP (TaBleSPoon)
- The Louvre
- The Oz Museum
- The Strong National Museum of Play
- They Can Talk
- This Beat Goes on/Switchin' to Glide
- Tick Removal (CDC)
- Trappistine Candy
- Vacation Rentals By Owner
- Vehicle Privacy Report
- VPNFilter Check
- War Puppets Rise to Heaven
- Weather Back Home
- WebGL Water
- Whalers on the Moon
- What's New on Netflix
- Who's On First
- Why are Jacks called Jacks?
- Wild Spirit
- Window Swap
- WKRP Turkey Drop
- Wordcount
- World's Hottest Chocolate Bar
- WWII Portraits of Honor
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- July 2011
- June 2011
- May 2011
- April 2011
No, Can You?
Posted in Because I Can, Humor
Congress adopts the Stars and Stripes
During the American Revolution, the Continental Congress adopts a resolution stating that “the flag of the United States be thirteen alternate stripes red and white” and that “the Union be thirteen stars, white in a blue field, representing a new Constellation.” The national flag, which became known as the “Stars and Stripes,” was based on the “Grand Union” flag, a banner carried by the Continental Army in 1776 that also consisted of 13 red and white stripes. According to legend, Philadelphia seamstress Betsy Ross designed the new canton for the Stars and Stripes, which consisted of a circle of 13 stars and a blue background, at the request of General George Washington. Historians have been unable to conclusively prove or disprove this legend.
With the entrance of new states into the United States after independence, new stripes and stars were added to represent new additions to the Union. In 1818, however, Congress enacted a law stipulating that the 13 original stripes be restored and that only stars be added to represent new states.
On June 14, 1877, the first Flag Day observance was held on the 100th anniversary of the adoption of the Stars and Stripes. As instructed by Congress, the U.S. flag was flown from all public buildings across the country. In the years after the first Flag Day, several states continued to observe the anniversary, and in 1949 Congress officially designated June 14 as Flag Day, a national day of observance.
Posted in Anniversary, On This Day, Patriotic
Niagara Falls Stopped Flowing
On June 12, 1969, after flowing continuously for over 12,000 years, the American Falls stopped.
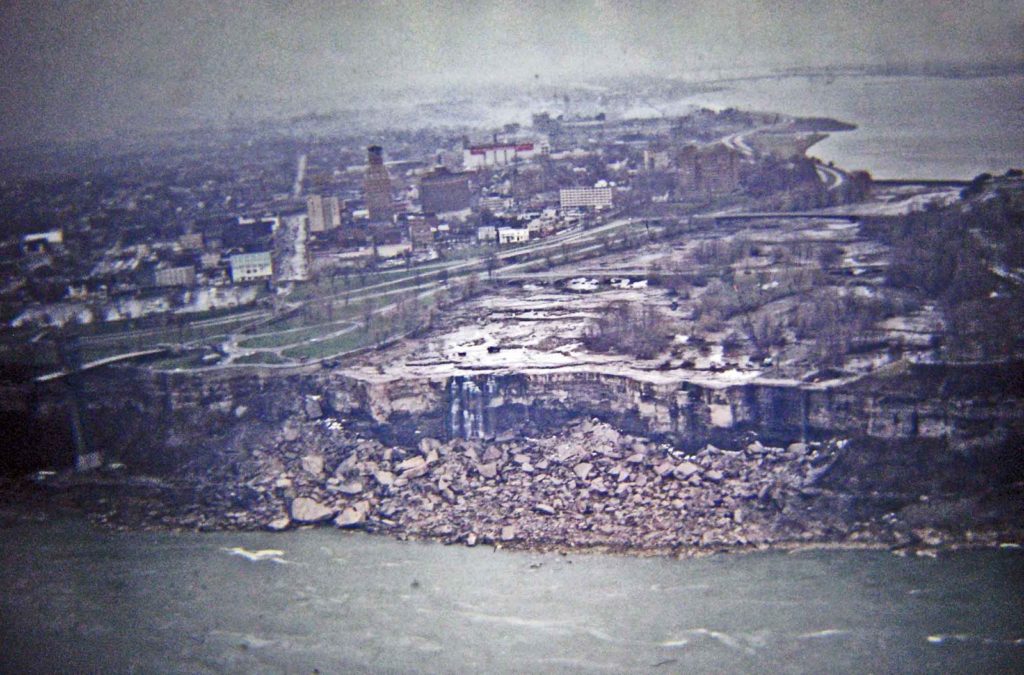
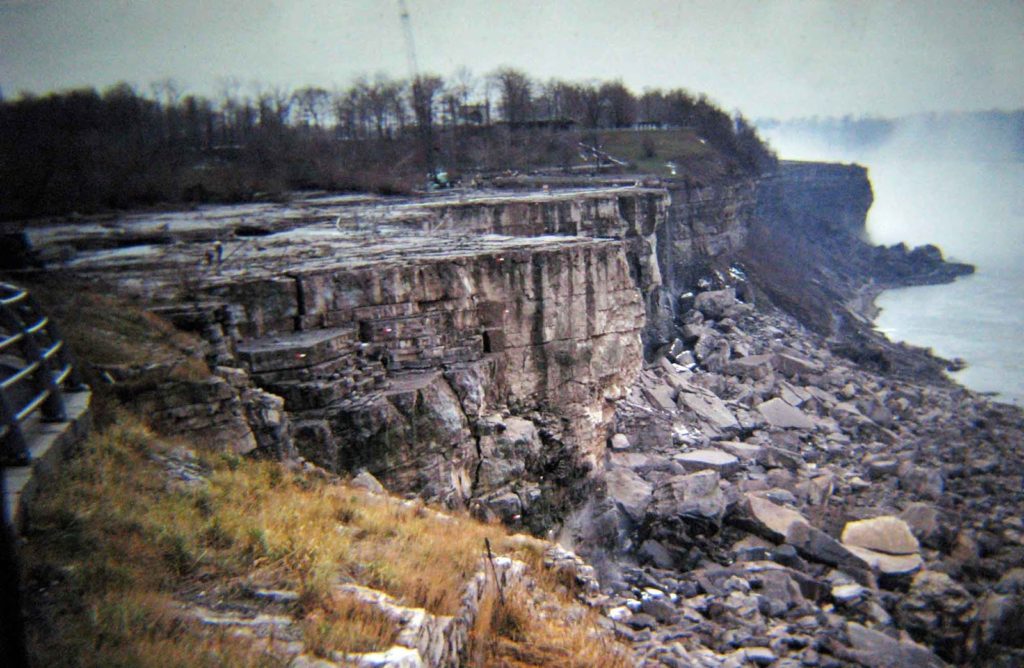


Read the entire story at rarehistoricalphotos.com, it is amazing!
Posted in Anniversary, On This Day
40th Anniversary of Ghostbusters
Ghostbusters is a 1984 American supernatural comedy film directed by Ivan Reitman and written by Dan Aykroyd and Harold Ramis. It stars Bill Murray, Aykroyd, and Ramis as Peter Venkman, Ray Stantz, and Egon Spengler, three eccentric parapsychologists who start a ghost-catching business in New York City. It also stars Sigourney Weaver and Rick Moranis, and features Annie Potts, Ernie Hudson, and William Atherton in supporting roles.
Posted in Anniversary, Because I Can, The Big Screen
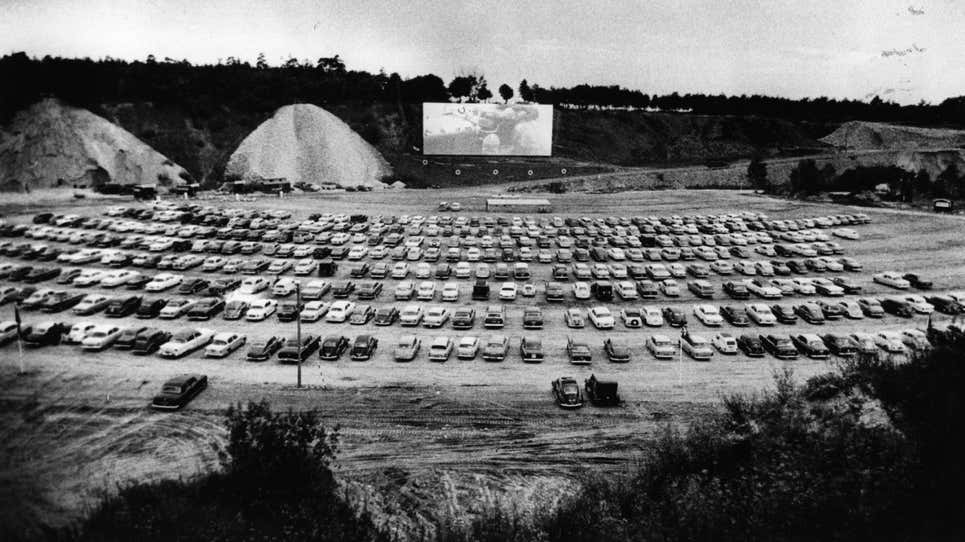
First Drive-in Theater
On the evening of June 6, 1933, motorists crowded into a parking lot on Crescent Boulevard in Camden, New Jersey for the first ever drive-in movie screening. And with that, the drive-in theater craze was born.
Posted in Anniversary, Because I Can, Planes Trains and Automobiles
Anniversary of WarGames
Posted in Anniversary, On This Day, The Big Screen
The True Size of Countries (Mercator projection)
Truesize.com will allow you to select and “copy” countries around the map adjusting for the Mercator projection (which is an interpretation of a 3d globe onto a 2d map). Awesome!
Posted in Because I Can
Happy Birthday, Big Ben
The famous tower clock known as Big Ben, located at the top of the 320-foot-high St. Stephen’s Tower, rings out over the Houses of Parliament in Westminster, London, for the first time on this day, May 31st, in 1859.
After a fire destroyed much of the Palace of Westminster–the headquarters of the British Parliament–in October 1834, a standout feature of the design for the new palace was a large clock atop a tower. The royal astronomer, Sir George Airy, wanted the clock to have pinpoint accuracy, including twice-a-day checks with the Royal Greenwich Observatory. While many clockmakers dismissed this goal as impossible, Airy counted on the help of Edmund Beckett Denison, a formidable barrister known for his expertise in horology, or the science of measuring time.
Denison’s design, built by the company E.J. Dent & Co., was completed in 1854; five years later, St. Stephen’s Tower itself was finished. Weighing in at more than 13 tons, its massive bell was dragged to the tower through the streets of London by a team of 16 horses, to the cheers of onlookers. Once it was installed, Big Ben struck its first chimes on May 31, 1859. Just two months later, however, the heavy striker designed by Denison cracked the bell. Three more years passed before a lighter hammer was added and the clock went into service again. The bell was rotated so that the hammer would strike another surface, but the crack was never repaired.
The name “Big Ben” originally just applied to the bell but later came to refer to the clock itself. Two main stories exist about how Big Ben got its name. Many claim it was named after the famously long-winded Sir Benjamin Hall, the London commissioner of works at the time it was built. Another famous story argues that the bell was named for the popular heavyweight boxer Benjamin Caunt, because it was the largest of its kind.
Even after an incendiary bomb destroyed the chamber of the House of Commons during the Second World War, St. Stephen’s Tower survived, and Big Ben continued to function. Its famously accurate timekeeping is regulated by a stack of coins placed on the clock’s huge pendulum, ensuring a steady movement of the clock hands at all times. At night, all four of the clock’s faces, each one 23 feet across, are illuminated. A light above Big Ben is also lit to let the public know when Parliament is in session.
Posted in Anniversary, Because I Can, On This Day
Happy Birthday, Clint Eastwood!
Clint Eastwood is an American film actor, director, producer, composer, pianist, businessman, investor, and politician. Eastwood first came to prominence as a supporting cast member in the TV series Rawhide.
Read morePosted in Anniversary, The Big Screen
Happy Birthday to the Man of 1000 voices
Mel Blanc (born Melvin Jerome Blank, May 30, 1908 – July 10, 1989) was an American voice actor and radio personality. After beginning his over-60-year career performing in radio, he became known for his work in animation as the voices of Bugs Bunny, Daffy Duck, Porky Pig, and most of the other characters from the Looney Tunes and Merrie Melodies theatrical cartoons during the golden age of American animation.
He later voiced characters for Hanna-Barbera’s television cartoons, including Barney Rubble on The Flintstones and Mr. Spacely on The Jetsons. During the golden age of radio, Blanc also frequently performed on the programs of comedians, including Jack Benny, Abbott and Costello, Burns and Allen, The Great Gildersleeve, and Judy Canova.
Blanc was nicknamed “The Man of a Thousand Voices”, and is regarded as one of the most influential people in the voice acting industry.
Posted in Anniversary, Because I Can, The Little Screen (Television)